Your Custom Text Here
Can CranioSacral Therapy Help Multiple Sclerosis?
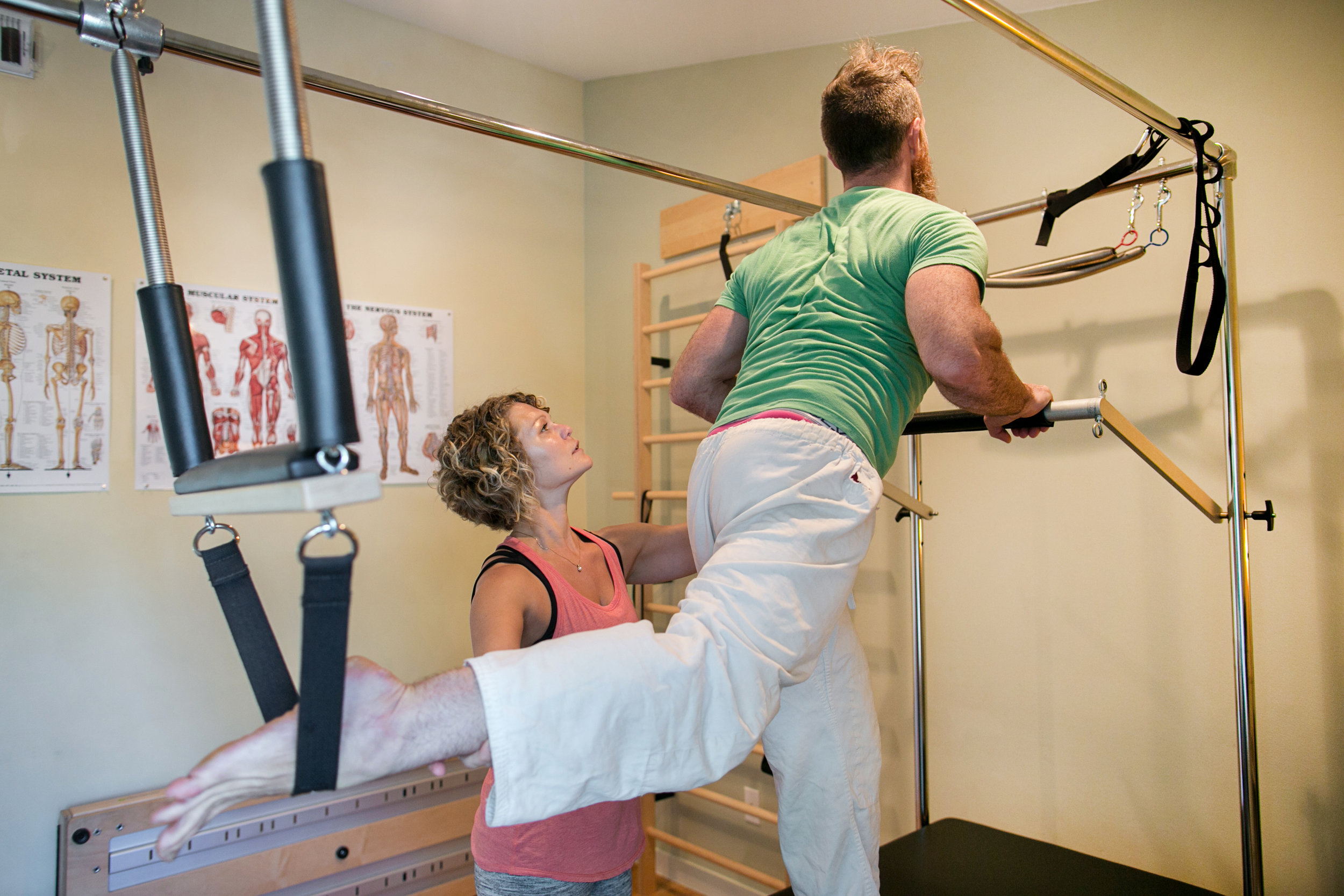
Last fall I set out to do a case study on a friend who has advanced Multiple Sclerosis (MS). His health took a more steep dip in 2020 to the point where he found day-to-day activities like walking and showering more challenging. CranioSacral Therapy (CST) has helped me immensely in healing from severe head trauma as a child, and I’ve seen it do wonders for my clients with histories of physical as well as emotional trauma. I wanted to see if it would help my friend and his symptoms related to MS.
Multiple Sclerosis is an autoimmune condition without a known cure where the immune system attacks the myelin sheath of the body’s nerves. Common symptoms include chronic pain, difficulty moving, vision and speech issues as well as anxiety/depression. CranioSacral Therapy (CST) is a gentle, hands-on technique that seeks to improve the function of the Central Nervous System and other body systems that relate to it, including the Immune System. If the Sympathetic Nervous System remains activated for long periods of time (as it would with chronic stress and/or trauma), it also affects the ability of the Immune System to do its job properly. Side note that this is why so many folks with autoimmune conditions also have trauma/PTSD backgrounds, or that a stressful event(s) triggers a condition. So, can and did CST help my friend and his pain?
A little background on my study subject: 63 year-old-male, diagnosed with MS in 2010 in tandem with optical neuritis and vertigo. We did the basic, 10 Step CST protocol, administered 8 weeks in a row, with steps in the same order over the course of a 60-minute session. I used the McGill Pain Questionnaire, a self-reported survey, which delineates different types of pain and ascribes a number for an individual’s pain level—that way we could quantify whether or not the work helped him. Maximum possible score is 78; the higher the number, the more pain the individual is experiencing.
When we began the study, he reported a pain level of 62 out of 78 and most acutely felt pain in the lower back and hip regions with spasticity. He also felt a concentration of pain in how his mental health was impacted, experiencing fear as well as intense to unbearable pain (these were boxes on the questionnaire).
After 8 weeks, he reported a 60% improvement in pain (37 of 78) with less tension and numbness. How the pain affected his mental health was the most significant area of improvement. Initially, he selected adjectives such as agonizing and dreadful (higher on the pain scale) whereas in the second evaluation he only selected nagging (the lowest). In general, he felt more calm, less anxious and was experiencing better quality of rest. Another note here, we did this study in the 8 weeks preceding the election. So, the fact that he had a greater sense of ease is even more telling of the work and how it can help you or someone you know.
A lot of massage therapists and chiropractors are trained in this technique. If you have a history of anything I mentioned: PTSD, trauma, concussion and/or autoimmune issues, try a few sessions of CranioSacral to see if it helps your mental and physical health. It’s super relaxing—promise you’ll have a good sleep that night.
The Body Keeps Score
Did you know that if you (or someone you know) have suffered through abuse, a traumatic event or upbringing that the brain actually shifted as you (they) attempted to process the pain? This book has rocked my world the past couple of weeks in learning how amazing the body is and how healing from trauma is a layered process.
What is trauma?
In short, something that was stressful in which you felt alone. Obvious examples here include abuse, natural disaster, loss, terrorism and war. In looking at the behavioral patterns that can arise from trauma, I can't help but think most of us could cite some form of traumatic event(s)/relationship(s) in our lives.
How does the brain shift?
Trauma can actually change the brain's alert system and responding hormones in addition to leaving a mark on the brain similar to a stroke. The author, Bessel Van der Kolk, conducted a study where he showed participants images to trigger their trauma while monitoring their brain hemispheres. When participants were exposed to traumatic images, the right side of the brain that impacts how we perceive the world around us was activated, while the left, organizational side deactivated. The brain itself is in response mode to the trigger without real context of time or place. Moreover, the brain's response to trauma is pre-verbal so this explains why recounting what happened in a logical or coherent manner may be difficult or garbled.
While one may consciously choose not to respond to a trauma trigger, the body systems are still reacting, including hormones, which don't return back to normal levels after being in fight or flight or freeze mode. Because of this there is an internal disconnect so one may suffer from addiction or self-mutilation as well as illness, adrenal fatigue, fibromyalgia/chronic fatigue, poor sleep, memory issues, autoimmune disorders and irritability. (If you're super geeky about this stuff, as I am, he spends a good 10 pages going into brain chemistry specifics...but does so in a very approachable way for the brain science novice.)
What are some symptoms of trauma?
Hyper-vigilance-Because of the brain shift, one can be in a perpetual state of hyper-vigilance. This goes back to the perception lens--the brain is constantly surveying for a potential threat. This also means that one may project past traumas onto current life events.
Social isolation-Not wanting to engage with others because this could set off a trigger, so it's better to avoid interaction. On the flip side, fraternizing with those who have suffered the same trauma may feel safe (e.g. other veterans) yet this can also be limiting over time as one's identity shifts.
Loss of identity-You may more commonly know this as survivor's guilt as well as confusion if the person who abused you was supposed to be your caretaker/loved one.
Emotionally numb-A way to deal with the trauma is to disassociate from one's body and feelings, leaving one devoid of feeling.
Loss of imagination-If raised in an unsafe environment, all of the body's systems are in self-preservation (hyper-vigilance) mode so there's no room for imagination or exploration.
Risk-taking-The body releases endorphins which are like morphine, so one can become addicted to risks or even find pleasure in pain. The body seeks this out to overcome anxiety.
How does one heal?
The author suggests 3 approaches to be used in tandem as needed.
- Top down with talk therapy, specifically EMDR, Internal Family Systems and Neurofeedback. If you're in Austin, there's a great clinic that uses these approaches. Find out more about them here.
- Medications that will turn off the body's alarm systems.
- Bottom up through the physical so that the body can experience something other than helplessness and rage which gets held in the viscera (i.e. having a broken heart, stomach in knots). He suggests this in particular for those who suffer from musculo-skeletal pains that may have an emotional root. Since that is my bag and this is my blog, I'm going to spend a bit more time on this and his suggestions.
Heal trauma with mindfulness.
Ki Hara Active Stretching for mindfulness and flexibility.
The first step in releasing the past is reconnecting with and establishing ownership of the body to feel, find peace and focus so that when things trigger the past, one can maintain internal calm. When we can connect with how we feel, we can begin to change perspective. If we can't feel, we are incapable of figuring out what our body needs and how we can best take care of it. By being present in our bodies, it is safe to revisit the past without being overwhelmed by it. We can start to have words for things we may have hidden from ourselves and reintegrate the pieces of ourselves that we've lost along the way. A way of coping with trauma is disassociating from our bodies, so mindfulness and breath work reaffirm who we are as a whole being.
The author recommends yoga as an avenue to mindfully connect with the body. A former client of his specifically cited that Pilates helped her heal from a traumatic event to her pelvis. I love both of these modalities, yet I don't think I learned to be deeply connected to my own body until I encountered Ki Hara Resistance Stretching (aka yoga on steroids). It has been amazing for helping myself and my clients reconnect with areas of the body that have been forgotten and then integrating them to the whole. It's particularly effective because when I'm working with a client, it becomes a partner effort to rediscovery. In other words, it's not someone alone in their own stretching practice (though this is another component for establishing ownership of one's body). I can be an objective pair of eyes for how your body is moving when there could be a more efficient way. If you haven't connected to a part of your body in a long time, how are you even supposed to know it's there?
I found this book to be incredibly insightful both for my own understanding of some areas I need to work on and to have more compassion for others who have are trying their best to heal. If you're one who is better with video over books, here's an interview with the author with some similar themes.
An Energetic Approach to Movement
Movement is more than just muscles contracting to make bones move like we see in the gym machine pictures. Our body is a whole unit in which everything participates to create movement. For this reason, I approach the body from a fascial or connective tissue perspective which informs how various parts of the body work in conjunction to make the body shift and move. As I studied the human body, I observed subtle patterns of how things worked together and I could feel someone's jaw release as I stretched their quads (front thigh muscles). Imagine my excitement when I read Anatomy Trains in which Thomas Myers details all of these connections I was feeling. Even more neat is how these fascial lines also mirror Traditional Chinese Medicine/Acupuncture meridians or energetic pathways.
When someone steps into my studio, I immediately begin observing how these fascial lines may be locked too tight or too loose and how that is impacting their movement as well as contributing to pain they could be having. This means that your neck tension, for example, could be coming from a tight IT band. We then stretch and strenghten these other pulleys that could be pulling on a spot where the pain is felt.
This leads to more than just a muscular contraction approach to what is going on in the body both in terms of pain and improving athletic performance. Yoga and martial arts have understood this fluidity in movement approach for centuries. The cool part is you can actually become so connected to your body that you'll be able to feel how your foot tightening on one side is causing your shoulder blade to brace which may be impacting your tennis swing.
Employing the insight of fascial lines/acupuncture meridians and consciously moving through them helps to shift and move energy though the body. For some this may just feel like a muscular release or even a greater mindy body connection. This can also mean that you feel lighter on your feet as you walk and run, or maybe more relaxed and supported by the earth. You may find breathing easier or that you have more power. Some days this means that you can have an emotional release or even feel euphoria as you 'exercise'.
One of the beginnning concepts I teach is that we walk from the front of our low abs/pelvic muscles and that our shoulders balance into our solar plexus. So, it's kind of like we have a triangle from the pelvis to our legs and then if you flip that triangle up-side-down, your shoulders drop into your diaphragm. From an eastern perspective, we're walking from the 2nd chakra or lower dantian which also happens to be our pelvic muscles, the base of our core. Our shoulders nestle onto the shelf of our 3rd chakra or our middle dantian which is also our diaphragm, or the top of our core. Feeling these connections automatically means you're using your core in a fluid sense, instead of overly contracting these muscles, restricting the breath and tightening the hips. Connecting to the core in this way also helps to open these lower energy centers where many of us hold our emotional wounds.
An energetic approach to movement will leave you feeling more relaxed, open and supported which means more energy and less fatigue at the end of the day. Tapping into these connections always takes sports performance to a whole new level--you'll feel lighter as well as more agile. Schedule an appointment to learn how to tap more deeply into your personal power!
How strong are your respiratory muscles?
Take a moment and start counting the duration of your inhalation and exhalation. Does the pace at which you're breathing feel like your normal? Is it easier to inhale or exhale? Where do you find the breath entering and exiting? Does it most easily move in and out of your belly or your upper chest? Do your lower ribs move when you exhale? I find that most people don't move their lower ribs in the respiratory cycle, which means they're missing out on a full breath. This can go on for years and impacts pretty much every other system in your body, including your digestive and nervous systems.
How does the breath cycle work?
The diaphragm acts as a plunger system, pulling air into our bodies and filling our lungs (fun fact: the lungs are kind of like origami-folded tissue that unfolded are the size of a tennis court). The diaphragm is a muscle, so it has a full range of motion like any other muscle, yet most of us only 'exercise' it in a very short range. We shallowly breathe due to stress and holding a posture that we think is 'good', more on that in a moment. If you consider how the diaphragm typically works in this short cycle, it would be like doing thousands of tiny bicep curls all day long--sounds kind of funny when you think about it that way, right? The diaphragm is the main breathing muscle, yet there are several other secondary muscles that help out. One of my favorite groups is the intercostals. These muscles glide in beteeen each rib and help to expand and contract our rib cage. They are, however, weak for most folks.
How do the intercostals weaken and why should I take ever loving care of them?
As previously mentioned, most of us breathe shallowly as a stress-holding pattern. For some, this means weak and tight intercostals, so it's hard to inhale and expand them. For others, they're weak and puffed out (barrel-chested) and it's harder to exhale. In the latter case, I find that people assume this posture thinking they have good and confident posture--yet you can't breathe. Another way this pattern can occur is from sucking the stomach in or wearing restrictive clothing. Try sucking your stomach in right now and you'll feel your rib cage puff. Either way, we want these guys to be able to expand and contract fully, just like our biceps.
Strong intercostals and respiratory muscles help massage your stomach as you breathe, enabling your digestive system to do its thing. They also help to keep your nervous system at ease and not in fight-or-flight mode. As an added bonus, you're strethening your core muscles, which will give you organic, proper posture. If you're active, tapping into a full breath cycle, including the plunger power of your diaphragm, will take your athletic abilities to the next level.
How do I strengthen my respiratory muscles?
To start, be more conscious of your breath. I love the count breath. Try to equal out your inhalation and exhalation and then gradually add another count. Say you start at a 4 count, can you gradually reach your way to an 8? As you continue to add time, focus on squeezing the air out of your rib cage during the exhalation, contracting your intercostals.
You can also try these exercises over a towel, ball, pillow or foam roller.
I integrate breath work into my sessions with clients so that you can grow these muscles, bettering your digestive and nervous systems, while improving your posture and core. In finding your breath, you find your power!
What can you let go of in 2017?
As we begin another year, many of us take this time to reflect on our health. Wellness resolutions are made and often not adhered to after a few days or weeks. If we start to look at what we're ready to let go of over adding another thing to the list, those resolutions stick and we have longer-lasting health benefits.
When you start to see your physical health is also your emotional health is also your mental health, you'll have more profound results in your overall wellbeing. When life stress happens, we can mentally acknowledge what's going on, we emotionally feel a response, and the physical body goes into self-protection mode even if we don't consciously realize it. Mindfully connecting to your movement gives you greater dexterity in your physical body, while showing you which stressors and emotions you hold where so you can let that old stuff go!
I had my own journey making these mind-body connections after I had a stabbing pain in my left hip so intense (10 out of 10 pain) that it locked out my lower back. I wrote about this more here. I studied and figured out the muscular imbalances, but that didn't fully eradicate the pain. Unfortunately, it wasn't until more than a year later that I started to notice when my hip pain increased. It initially surfaced when my father unexpectedly died of a heart issue. So, anytime I felt threatened or afraid of losing someone, those muscles tensed. As I addressed this duality of emotion (fear) with my muscular imbalance, my hip got better. It has since reared its head a few other times, most abruptly and intensely when I had a miscarriage. So, same death and loss trigger.
Each time the pain has returned, it has been less instense or has not lasted as long because now I'm working through the root triggers. We often don't realize how much we're internalizing minute-to-minute until something hurts. In my case, the grief was so overwhelming I couldn't even process what I was or was not internalizing. Now when my hip starts to 'talk' to me, it's my reminder to take stock of what is going on in my life...what am I afraid of? Is there another emotion my body is responding to? Can I shift my mental perspective?
In my work with clients, we try to explore which emotions you're experiencing and holding onto in your injured and chronically stuck spots. You may not completely let go of something you're holding onto, there are layers to process, particularly for intense or tragic life experiences. At least in letting go, we allow more space for healing and more of us is freed up to be present and more authentic. We have more ability to create the life we want over physically carrying around the past.
What are you ready to let go of this year?
For the month of January, I'm offering a New Year's package for new clients. For more information, click here.